The structure of atoms is able to be understood if one considers the light within the atom is produced by geometric features of the atom itself. There is a point of reference. An inertial frame of reference that does not change at (0,0,0). The point of the singularity.
Atomic structure and the light housed within the atom
-
Orbitals
The s orbitals are important to understand the right-hand rule of electromagnetism. At 90 degrees there are four points in a circle of 360 degrees. If we only consider s orbitals to contain electrons, then hydrogen only has one electron in the orbital layers of the atom. This is the simplest form to think of the proton and the electron and the neutral basis of the atom. However, it is more complex than you realise.
-
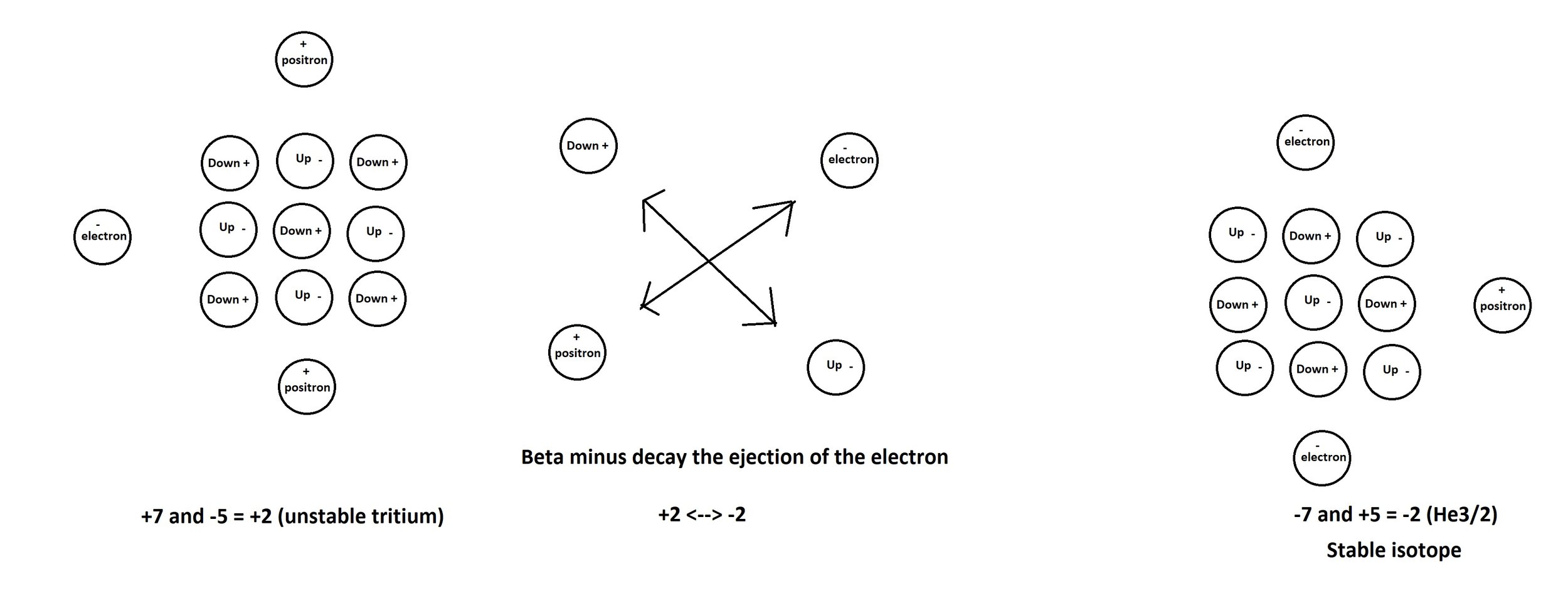
Duality, the mirror stability state
The universe maintains its ability to generate fundamental particles by turning fields of energy into structure by the tension between two different velocities c and v.
-

Missing anti-matter
There is a problem in physics and cosmology regarding the missing anti-matter. A baryonic asymmetry. What this means is 95% of the universe remains hidden. What is dark energy and dark matter? We have an answer to the missing 95% of the universe that did not require measurement but an ability to think logically.
Baryonic asymmetry
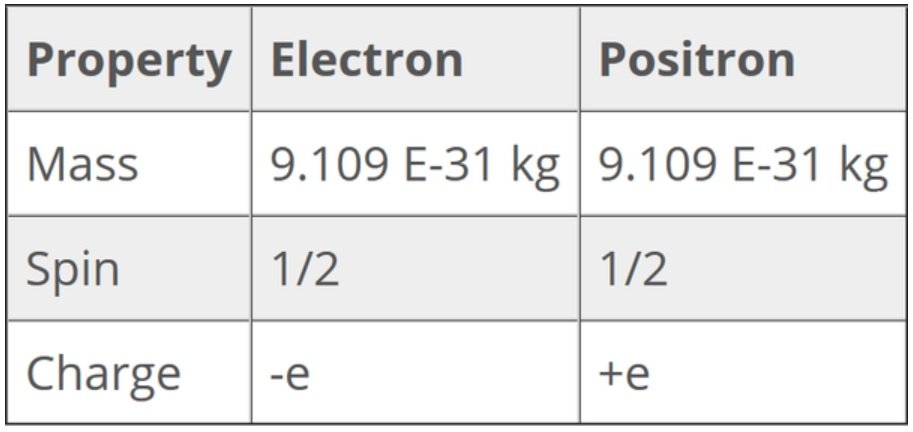
It comes down to the quark charge calculations and maintaining charge parity with positron and electron pairs. If you cannot understand the presence of positrons within atomic structure, I am afraid you have been led astray by measurement and the use of fractions and additions. By using whole numbers the calculations for quark charges is realigned with positron and electron charges.
Baryonic asymmetry is a big problem in cosmology. The missing antimatter. The reason why the Standard Model of particle physics is missing something